The Indian Contract Act, 1872, introduces several key terms and definitions that are crucial for understanding and applying the law of contracts. Here are some of the most important terms and their definitions:
Contract:Indian Contract Act 1872
- Definition: An agreement enforceable by law.
- Section: Section 2(h)
Agreement:
- Definition: Every promise and every set of promises, forming the consideration for each other.
- Section: Section 2(e)
Promise:
- Definition: When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or to abstain from doing anything, with a view to obtaining the assent of that other to such act or abstinence, he is said to make a proposal.
- Section: Section 2(b)
Proposal (or Offer):
- Definition: When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or to abstain from doing anything, with a view to obtaining the assent of that other to such act or abstinence, he is said to make a proposal.
- Section: Section 2(a)
Acceptance:
- Definition: When the person to whom the proposal is made signifies his assent thereto, the proposal is said to be accepted. A proposal, when accepted, becomes a promise.
- Section: Section 2(b)
Consideration:
- Definition: When, at the desire of the promisor, the promisee or any other person has done or abstained from doing, or does or abstains from doing, or promises to do or to abstain from doing, something, such act or abstinence or promise is called a consideration for the promise.
- Section: Section 2(d)
Void Agreement:
- Definition: An agreement not enforceable by law.
- Section: Section 2(g)
Voidable Contract:
- Definition: An agreement which is enforceable by law at the option of one or more of the parties thereto, but not at the option of the other or others.
- Section: Section 2(i)
Void Contract:
- Definition: A contract which ceases to be enforceable by law becomes void when it ceases to be enforceable.
- Section: Section 2(j)
Contingent Contract:
- Definition: A contract to do or not to do something if some event, collateral to such contract, does or does not happen.
- Section: Section 31
Quasi-Contract:
- Definition: Certain relations resembling those created by contract, obligations are imposed by law as if there were a contract.
- Section: Sections 68 to 72
Reciprocal Promises:
- Definition: Promises which form the consideration or part of the consideration for each other.
- Section: Section 2(f)
Consent:
- Definition: Two or more persons are said to consent when they agree upon the same thing in the same sense.
- Section: Section 13
Free Consent:Indian Contract Act 1872
- Definition: Consent is said to be free when it is not caused by coercion, undue influence, fraud, misrepresentation, or mistake.
- Section: Section 14
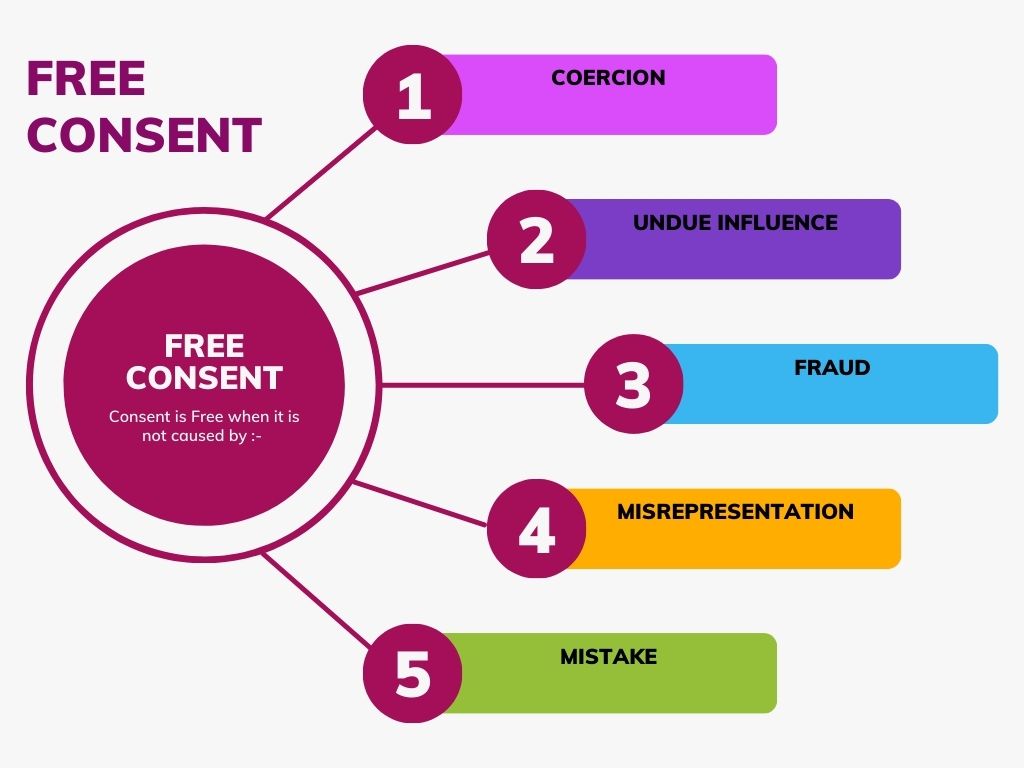
Coercion:
- Definition: Committing or threatening to commit any act forbidden by the Indian Penal Code or the unlawful detaining or threatening to detain any property, to the prejudice of any person whatever, with the intention of causing any person to enter into an agreement.
- Section: Section 15
Undue Influence:
- Definition: A contract is said to be induced by undue influence where the relations subsisting between the parties are such that one of the parties is in a position to dominate the will of the other and uses that position to obtain an unfair advantage over the other.
- Section: Section 16
Fraud:Indian Contract Act 1872
- Definition: Fraud means and includes any act committed by a party to a contract with intent to deceive another party thereto or his agent, or to induce him to enter into the contract.
- Section: Section 17
Misrepresentation:
- Definition: A misrepresentation is when a person makes a false statement, believing it to be true, or without knowing it to be false, with the intention to induce the other party to enter into a contract.
- Section: Section 18
Breach of Contract:
- Definition: A breach of contract occurs when one party fails to perform their obligations under the contract.
- Remedies: Damages, specific performance, injunction, etc.
- Sections: Sections 73 to 75

